Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is a device that measures the three-axis attitude angle (or angular rate) and acceleration of an object. The gyroscope and accelerometer are the core devices of the inertial navigation system. With the help of the built-in acceleration sensor and gyroscope, the IMU can measure linear acceleration and rotational angular rate from three directions, and obtain information such as the attitude, speed and displacement of the carrier through calculation.
IMU can obtain information about the carrier's attitude, speed, and displacement. It is widely used in the fields of automobiles and robots, and it is also used in occasions that require precise displacement calculations with attitude, such as submarines, airplanes and other inertial navigation equipment. IMU based on MEMS technology, as well as MEMS inertial sensors, will be the focus of future development.
Definition and function of IMU
According to the P1559 standard being revised by the IEEE Association of the United States, the inertial measurement unit is defined as "a device that can measure three-dimensional linear and angular motion without external reference." Under normal circumstances, each inertial measurement device contains three sets of gyroscopes and acceleration sensors, which measure the angular acceleration and linear acceleration of three degrees of freedom respectively, and obtain the object's position in space through the integration of acceleration and the superposition of initial velocity and position. The direction and speed of the movement in the inertial navigation system are combined with the setting of the movement track in the inertial navigation system to correct the heading and speed to realize the navigation function. ERICCO IMUs deliver the highest performance and richest feature set on the market. And IMUs are built to the highest quality standards to endure the test of time in the most difficult conditions. You can rely on our products.
Currently, IMUs currently on the market are mainly 6-axis and 9-axis. The 6-axis IMU includes a three-axis acceleration sensor and a three-axis gyroscope; the 9-axis IMU has an additional three-axis magnetometer. In addition, for IMUs using MEMS technology, a thermometer is generally built-in for real-time temperature calibration. Like ERICCO ER-IMU-M01 High Performance MEMS IMU is 6-axis IMU, through the built-in accelerometer and gyroscope, the IMU can measure linear acceleration and rotational angular velocity in three directions, and obtain the attitude, velocity and displacement information of the carriers.
Whether it is a 6-axis or 9-axis IMU, it can output three-dimensional angular velocity signals and acceleration signals in real time to calculate the current posture of the object. This has important application value in platform stability and navigation.
IMU application on the car
IMU is mostly used in equipment that requires motion control, such as automobiles and robots, and are also used in occasions that require precise displacement calculations with attitude, such as inertial navigation equipment for submarines, airplanes, missiles, and spacecraft. Compared with other navigation systems, the inertial navigation system has important characteristics such as comprehensive information, complete autonomy, high concealment, real-time and continuous information, and is not subject to time, geographical restrictions and human factors interference. It can be used in the air, water, underground, etc. Work normally in various environments.
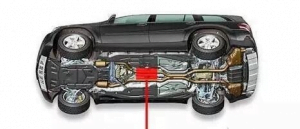
For example, the above-mentioned advantages of IMU are particularly obvious in autonomous driving systems. In the autonomous driving system, IMU can be used as an effective supplement when other sensor data is missing. By calculating the vehicle's attitude (pitch and roll angle), heading, speed and position changes, IMU can be used to fill the gap between GNSS signal updates, and even dead reckoning when GNSS and other sensors in the system fail. Therefore, as an independent data source, IMU can be used for short-term navigation and to verify information from other sensors.Such as ER-IMU-M01A through the built-in accelerometer and gyroscope, the IMU can measure linear acceleration and rotational angular velocity in three directions, and obtain the attitude, velocity and displacement information of the carriers.
IMU application in autonomous driving system
The principle of IMU is very similar to walking small steps in the dark. In the dark, due to the error between your own estimation of the step length and the actual distance you walked, as you take more and more steps, the difference between your estimated position and the actual position will become farther and farther. When taking the first step, the estimated position is still relatively close to the actual position; however, as the number of steps increases, the difference between the estimated position and the actual position becomes larger and larger. According to this method, it is extended to three-dimensional, which is the principle of inertial measurement unit.
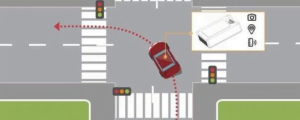
The academic expression is: Based on Newton's laws of mechanics, by measuring the acceleration of the carrier in the inertial reference frame, integrating it with time, and transforming it into the navigation coordinate system, the velocity in the navigation coordinate system can be obtained. , Yaw angle, position and other information.
Inertial sensor market
The development of inertial sensors directly determines the development and application of inertial navigation systems. The cost, volume and power consumption of inertial sensors themselves affect the corresponding parameter indicators of inertial navigation systems. The development of inertial measurement sensors needs to weigh the following factors: accuracy, continuity, reliability, cost, volume/weight, and power consumption.

At present, ERICCO’S IMU is mostly used in motion control equipment, such as vehicles and robots, and can also be used in occasions that require the use of attitude calculation for accurate displacement, such as inertial navigation equipment for submarines, aircraft, missiles and spacecraft.
In the downstream civilian market of inertial navigation, the applications of inertial sensors cover the fields of geodetic surveying, oil drilling, electronic transportation, automobile safety, consumer electronics, etc. Among them, MEMS inertial sensors are the most widely used in the consumer market. At the same time, small, low-cost MEMS inertial sensors and high-precision, high-performance sensors will be the focus of future development.
Founded in 2006, Ericco is an industry leader with rich product experience in the field of Inertial measurement unit &Inertial navigation system &north finder
I/F conversion circuit
V/F conversion circuit
FOG Inertial measurement unit
MEMS Inertial measurement unit
MEMS Inertial navigation system
inertial survey system
integrated navigation system
Attitude Heading Reference System (AHRS)
gyro theodolite
More Technical Questions
2.What are the advantages of MEMS IMU?
3.Application of MEMS IMU in Automobile
4.Research Background and Current Status of MEMS IMU
6.The Difference Between Gyroscope, Compass, IMU, MEMS
Products in Article