With the development of sensors today, miniaturization, intelligence and integration are the only way to upgrade. Today, let's introduce the mini products of the sensor family— MEMS sensor.
What is a MEMS sensor?
The full name of MEMS is Micro-Electromechanical System. Micro-electromechanical system refers to a micro-device or system that can be produced in batches and integrates micro-mechanism, micro-sensor, micro-actuator, signal processing and control circuit, interface, communication and power supply on one or more chips. MEMS sensor is a new type of sensor manufactured by microelectronics and micromachining technology.
MEMS is an advanced manufacturing technology developed on the basis of semiconductor manufacturing technology with traditional semiconductor technology and materials. MEMS mainly involving micromachining technology, mechanics/solid acoustic theory, heat flow theory, electronics, materials, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, and so on. After more than 40 years of development, it has become one of the major scientific and technological fields attracting worldwide attention.
Applied materials:
Silicon-based materials: Most of the raw materials of integrated circuits and MEMS are silicon (Si), which can be extracted in large quantities from silicon dioxide. What is silicon dioxide? To be more popular, it is sand. After a series of complex processing, the sand became monocrystalline silicon.
The material mainly made of silicon has excellent electrical properties. The strength and hardness of silicon material are equivalent to that of iron, the density to aluminum, and the thermal conductivity to molybdenum and tungsten. If the area of a single MEMS sensor chip is 5 mm x 5 mm, an 8-inch (20 cm in diameter) wafer can cut about 1000 MEMS chip gyroscopes, and the cost allocated to each chip can be greatly reduced.
Non-silicon materials: In recent years, the material application of MEMS has been gradually replaced by non-silicon materials. Academic researchers are now focusing on the development of polymer and paper-based micro devices. The devices developed with these materials are not only environmentally friendly but also simple in manufacturing equipment and low in cost. Compared with silicon materials, they have significantly reduced the R&D budget. Many innovations in polymer and paper-based micro-devices point to medical applications. For this field, biocompatibility and flexibility of materials are basic requirements.
The function and performance development of paper-based and polymer micro-devices is still in a relatively early stage, and the production facilities for such devices have not been developed yet. The maturity and commercialization of these new technologies may take more than 10 years. Therefore, there is still a lot of innovative work to be done in the research of micro-devices based on silicon materials. Otherwise, it will face the risk of stagnation.
Technical advantages:
MEMS technology is used to manufacture sensors, actuators or microstructures, which has the characteristics of miniaturization, integration, intelligence, low cost, high efficiency, mass production and high productivity. MEMS technology makes tens of thousands of MEMS chips (some processes also put integrated circuit chips in the same step) appear on every wafer.
This batch process has now been fully automated, isolating human factors, ensuring that the process error between each MEMS chip can be strictly controlled, thus improving the yield. After slicing and packaging, they become MEMS chips one by one. From the appearance, most MEMS chips and integrated circuit chips are similar.
To sum up, the characteristic size of micrometer magnitude enables MEMS sensors to complete some functions that cannot be achieved by traditional mechanical sensors. It is the main force of micro-sensors and is gradually replacing traditional mechanical sensors. It is widely used in consumer electronics, automotive industry, aerospace, machinery, chemical industry, medicine and other fields. Common products include pressure sensors, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and catalytic sensors.
Differences from traditional sensors:
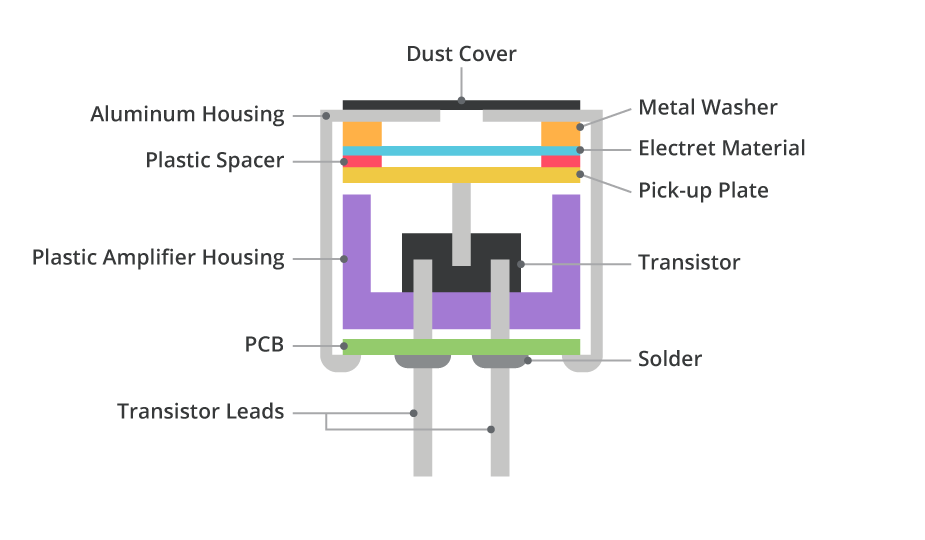
In the following picture, take microphone as an example to better understand the difference between traditional microphone and MEMS microphone.
Conventional electret microphone:
MEMS microphone:
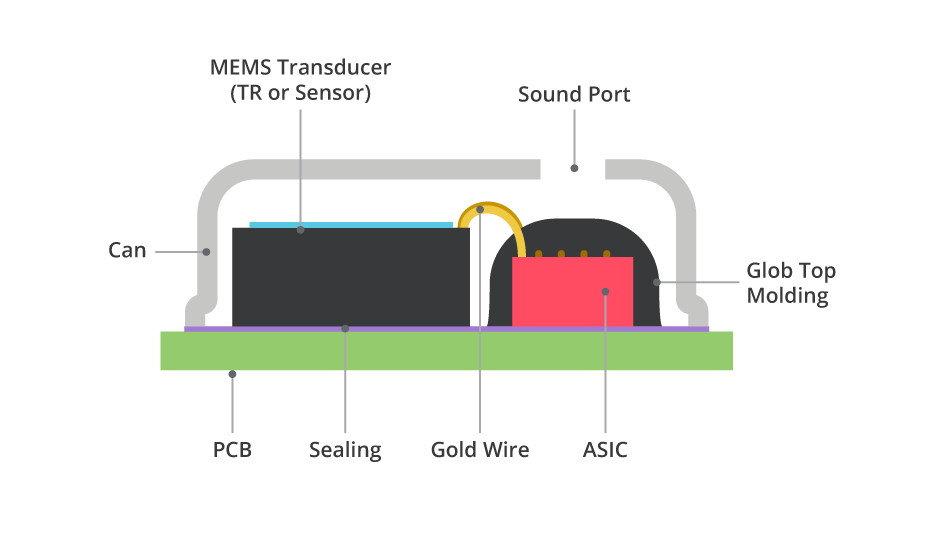
In the picture, seven or eight mechanical parts of the traditional microphone are all integrated on a small MEMS sensor chip, which is very small in size and light in weight. Because it is chip manufacturing, it has good consistency, low power consumption and is easier to mass production. But the technical requirements are very high. The emergence of MEMS sensors has greatly met everyone's requirements for small-size and high-performance of products.
There are different types of gyro sensors in the market. Ericco provides navigation level MEMS Gyro and north seeking level MEMS Gyro, which are small in size, light in weight and high in accuracy. If you want to know more about the technical problems of MEMS Gyro sensors, please feel free to contact us: https://www.ericcointernational.com/
More Technical Questions
1.Background and Development Status of MEMS Inertial Sensors
2.Analysis of Typical Applications of MEMS Sensors
3.MEMS Sensors Welding Process
4.Precision MEMS Sensors Realize New Navigation Applications
6.Determination of Initial Attitude Angle of MEMS Inertial Sensor
Products in Article