Landslides are complex geological phenomena influenced by various factors such as slope instability, weather conditions, and human activities. Monitoring these hazards is crucial for early detection and mitigation efforts to protect lives and infrastructure. GNSS technology, specifically its integration with monitoring equipment using GNSS chips, which relies on signals from satellite constellations to determine precise locations on Earth's surface, has emerged as a valuable tool for landslide monitoring.
1.The Role of GNSS Chips in Landslide Monitoring
Cost Reduction: GNSS chips serve as the core components of GNSS receivers used in landslide monitoring equipment. These chips have significantly reduced the cost of monitoring devices, making them more accessible for widespread deployment in landslide-prone areas. The affordability of GNSS chips has democratized access to advanced monitoring technology, enabling researchers, governments, and communities to implement proactive measures against landslide risks.
Miniaturization: The small size of GNSS chips allows for the development of compact and lightweight monitoring devices. These devices can be easily deployed in remote and inaccessible terrain, providing continuous monitoring of landslide-prone areas without the need for extensive infrastructure or manpower. The miniaturization of monitoring equipment enhances scalability and flexibility, enabling targeted monitoring efforts in high-risk zones.
Fig.1 Small GNSS Chip developed by Ericco WLCSP 1.70×2.84×0.5mm
Enhanced Performance: Despite their compact size, GNSS chips offer high-performance capabilities in terms of signal acquisition, tracking sensitivity, and data accuracy. Advanced signal processing algorithms embedded in GNSS chips ensure reliable positioning information, even in challenging environmental conditions such as dense vegetation or adverse weather. The enhanced performance of GNSS chips enables more accurate and timely detection of landslide-induced deformations, allowing for early warning and response measures to be implemented effectively.
2.Advancements in GNSS Chip Technology
Multi-Frequency Support: The latest generation of Ericco GNSS chips (show in Fig.1) supports multi-frequency signals from satellite constellations, including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou. Multi-frequency receivers offer improved resilience to signal interference and multipath effects, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of landslide monitoring data. These chips enable precise positioning and deformation measurements, allowing researchers to capture subtle changes in landslide behavior with greater sensitivity.
Integration with Sensor Networks: GNSS chips can be integrated with other sensor technologies, such as accelerometers and inclinometers, to create multi-sensor monitoring networks for comprehensive landslide analysis. By combining GNSS data with data from other sensors, researchers can gain deeper insights into the mechanisms driving landslide activity and improve the accuracy of hazard assessment models. The integration of GNSS chips with sensor networks enhances the robustness and versatility of landslide monitoring systems, enabling holistic approaches to landslide risk management.
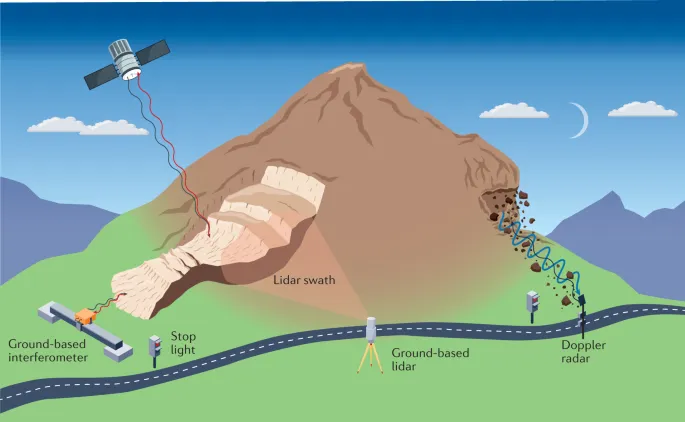
3.Challenges and Future Directions
Data Quality and Processing: Despite advancements in GNSS chip technology, challenges remain in ensuring the quality and reliability of monitoring data, particularly in harsh environmental conditions or areas with limited satellite visibility. Efforts are underway to develop robust data processing algorithms and quality control measures to address these challenges and improve the accuracy of landslide monitoring results.
Operational Considerations: The deployment and maintenance of GNSS monitoring networks require careful planning and coordination to ensure optimal coverage and data continuity. Operational challenges such as power supply, data transmission, and equipment durability need to be addressed to maximize the effectiveness of landslide monitoring efforts. Innovations in renewable energy sources, wireless communication technologies, and ruggedized monitoring equipment are helping to overcome these operational challenges and enhance the resilience of monitoring networks.
4.Conclusion
GNSS chips have revolutionized landslide monitoring by offering cost-effective, compact, and high-performance solutions for continuous deformation monitoring. These chips have enabled researchers and practitioners to implement proactive measures for landslide risk reduction, contributing to the safety and resilience of communities in landslide-prone areas.
It's worth noting that the ER-GNSS-C01/02 chip developed by Ericco has WLCSP dimensions of 1.70×2.84×0.5mm, with a data update rate of 1Hz, and a capture sensitivity of -147dBm and tracking sensitivity of -160dBm. Currently, the chip shows good performance in terms of volume, power consumption, and signal acquisition and tracking. The integration of GNSS nano-chip technology with RF baseband processing integration can effectively reduce the cost of GNSS monitoring equipment while also shrinking the device size, which is an important step in promoting the widespread application of GNSS monitoring devices in landslide hazard monitoring.
More Technical Questions
1. Quartz Flexure Accelerometer Pendulum Processing Technology
2. Choosing an Accelerometer - MEMS or Quartz Accelerometer
3. Driving Automotive Evolution: MEMS Accelerometers
4. Factors Affecting the Stability of Q-Flex Accelerometers
5. Structure Design of High Precision Quartz Flexible Accelerometer
6. Methods to Maintain the Long-Term Performance of Quartz Flexure Accelerometers






